How to use VirtualBox on Mac OS

Virtual machine is a unique piece of software which allows to simultaneously run several operational systems at once on your active OS, regardless whether it is Mac OS, Linux or Windows. Another advantage of such approach is that all the system work autonomously, externally one from another, and you may handle all of them in a distinct way. In this article I’m going to tell about specific features of running VirtualBox on Mac OS, what are the technical requirements for Mac platform, and what are the post installation issues you would need to handle in order to process the operations in VM successfully.
Here are the pre-requisites for the installation of the product on the platform from Apple, and what you need for the successful running of the Windows system in the VirtualBox app:
- you will an Intel-based Mac with 512Mb of RAM (1GB or more amount of operational memory is especially recommended)
- you will also require about 150 Mb of disk space, as of VirtualBox 5.1 (the latest version of the product, available on the moment of writing this article)
- in addition, about 5-10GB of disk space should be allocated for each virtual machine installed (in my case, Windows).
How to create and setup VM instance for the Windows OS?
Before using the emulated OS on your VirtualBox, you should first create the VM instance prior to running the virtual system on your Mac. Run the app and click “New” button on the toolbar. Starting from now the “Create New Virtual Machine” wizard is started. Click on “Next”.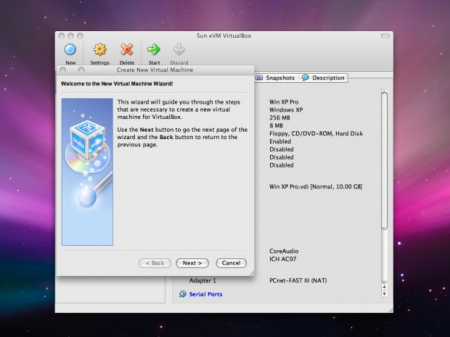
- when the “Memory” page is opened, set the RAM amount to 256 MB or more if you desire. Make thorough attempt not to overcome the level of 25-30% of your common RAM-memory, as far as it makes your OS X system run slower. Windows is quite a consumable environment, so pay attention to this while emulating
- as soon as the new page appears, enter the value “Windows 7” (or the version of Windows OS, which suits you best) and choose “Windows 7” from drop-down list “OS Type”. Click “Next” to go on
- in order to customize Windows, you would need to generate a virtual HDD. Click on “New” button, and as a consequence the HDD-creation wizard will be started
- among several options of hard disk type choose the “Dynamically expanding image” variant. Such a choice will help to save precious disk space from growing following the requirements
- leave the “Location” and “Size” option values untouched on the following page
- on the “Summary” page click “Finish” button, and all the changes will be applied as a result.
Afterwards you will see, that new Windows system has been added to the list of VirtualBox primary window and its status is “Powered Off”.
Simply use the “Start” button from the toolbar in order to start processing the VM for the first time.
- precisely after you start the virtual machine the “First Run Wizard” is displayed. Click “Next” for the beginning
- on the “Select Installation Media” form select the corresponding device, which you desire to apply for Windows installing. As a rule, that is a DVD-disk, which you insert into the optical drive. If you possess the ISO-file with Windows distributive you may not burn it on the optical storage device and firmly choose it as the media for installing
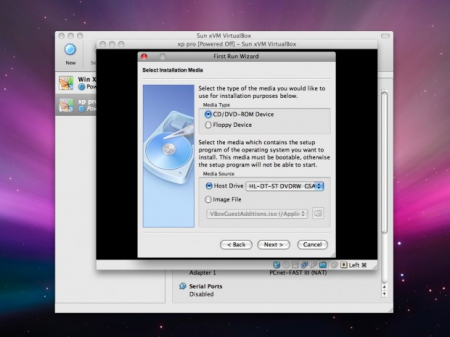
- as soon as the appropriate media is selected, complete the wizard by clicking the “Finish” button. In an instant the operational system will start booting
- in a second you will notice, that the setup procedure of Windows OS is initiated and you can go on with it as with any default setup routine. It may take several minutes from you, so keep patient and prepare a cup of black tea to have while waiting.
Post Installation Issues
Setting Up the Guest Additions
As soon as the Windows customization routine is completed, at first you require to set up the “Guest Additions” package. As you understand, Windows OS is just a basis for working with virtual machine, but it has a lot of cornerstones and pitfalls. One of such containable parts is Guest Additions package.
Basically, it contains system apps and device drivers for the guest Windows OS, which optimize the system for more optimal usability and performance. In short, it is a simple ISO-image file which is mounted and installed into the guest OS for maintaining additional functions and features.
Here’s what you should do in order to install VirtualBox Guest Additions on your VM instance:
- run the Windows OS
- select the “Devices” node in the upper menu and pick the “Install Guest Additions” item from the category
- go on with the setting up routine and reboot the operational system when the prompt appears.
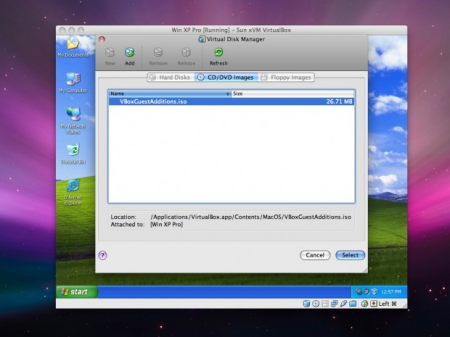
Making USB and Sound Support Enabled
It’s hard to imagine working in virtual environment without proper USB-connection and sound support. For the safety and protection USB and sound are disabled by default in VirtualBox, and you are ought to perform some specific actions in order to make them enabled in the guest operational system.
- turn off the Windows VM if it is runnable. That will be an ordinary Windows shutdown, so don’t worry to receive some unexpected issues after the turning the machine off. As an alternate method, you may simply close the main Windows form as a standard window and select the corresponding item from the list to cease the guest operability
- press the “Settings” button on the toolbar
- on the “Audio” tab, check out the “Enable Audio” option and pick the “Core Audio” value as primary host audio driver
- on the “Ports” tab mark up the “Enable USB 2.0 (EHCI) Controller” and “Enable USB Controller” checkboxes
- click OS in order to the performed changes to be applied.
After you run Windows the next time, you will be able to hear the sounds of entering the Windows OS, listen to the music and run games with audio. Also, the USB-devices will successfully be accessed. Afterwards you may require to pull out or eject the USB-gadget or disk from your Mac host OS in order to make it working in the emulated VM.
Thus, earlier I described the basic steps how to use VirtualBox on Mac OS. Moreover, I described the pitfalls of setting up the audio and USB-devices support on the guest OS, as well as peculiarities of VirtualBox Guest Additions package installation. Hopefully, it will serve you well in any situation and case.

Similar Materials